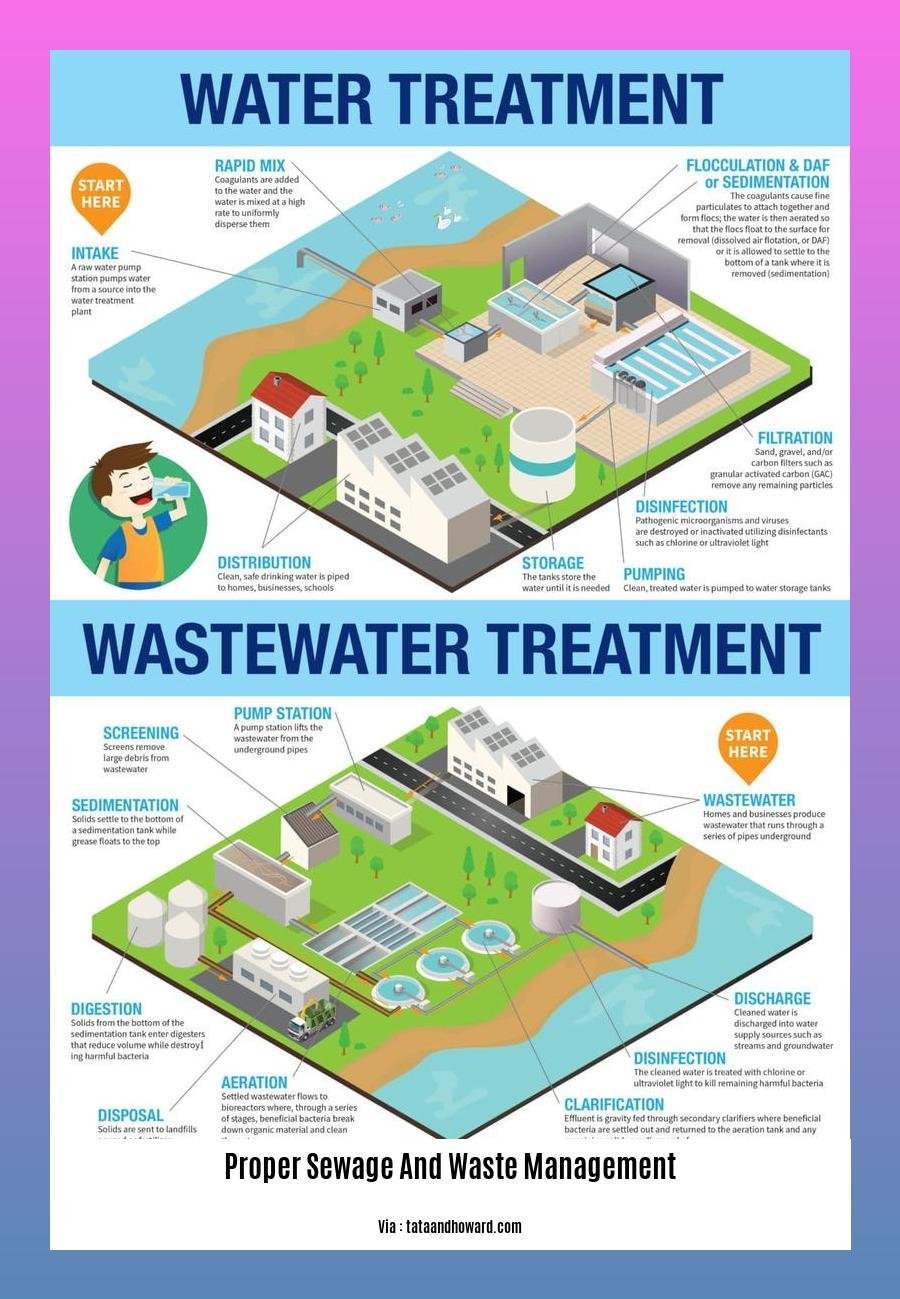
The Importance of Proper Sewage and Waste Management for Environmental Sustainability
Key Takeaways:

- Sanitation crisis: Most urban and rural communities lack effective systems to prevent human contact with waste.
- Health risks: Untreated sewage poses serious health risks, exposing populations to pathogens and diseases.
- Environmental damage: Sewage pollution degrades aquatic ecosystems and contaminates water bodies.
- Waste management goals: Focus on reducing waste and proper management of unavoidable waste.
- Worker safety: Proper sewage handling is essential to prevent disease transmission among sanitation workers.
Proper Sewage and Waste Management
What’s proper sewage and waste management?
Proper sewage and waste management involve collecting, treating, and disposing of wastewater and solid waste in ways that protect human health and the environment. It includes:
- Collecting wastewater from homes and businesses
- Treating it to remove contaminants
- Disposing of it safely so it doesn’t enter waterways or pollute the environment
- Reducing the amount of waste produced
- Recycling and composting waste
Why is proper sewage and waste management important?
Improper sewage and waste management:
- Contaminate water, soil, and air, posing health risks
- Contributes to climate change
- Hurts wildlife
- Can create unpleasant odors and attracts pests
Proper sewage and waste management:
- Protects public health
- Reduces pollution
- Conserves resources
- Improves quality of life
What can we do?
- Reduce waste by buying less and repairing or reusing items
- Recycle and compost what we can
- Properly dispose of hazardous waste
- Support businesses that prioritize sustainability
- Educate ourselves and others about the importance of proper sewage and waste management
Steps to Improve Sewage and Waste Management:
- Invest in infrastructure for sewage collection and treatment
- Promote sustainable waste disposal practices
- Educate the public about the importance of proper waste management
- Implement policies that encourage waste reduction and recycling
- Support research and development of innovative waste management technologies
The right to clean water and sanitation is essential for public health, poverty reduction, and sustainable development. Access to safe drinking water is a human right, and it is essential for good health and well-being. Water security and hygiene access are also essential for public health and sustainable development.
Economic Benefits of Effective Sewage and Waste Management
Here’s some trivia: would you believe that effective sewage and waste management can benefit the economy?
It’s true! Proper waste management practices can create jobs, conserve resources, and save money.
How Sewage and Waste Management Creates Jobs
Waste collection, treatment, and disposal require a workforce. Implementing effective waste management systems generates jobs in waste management companies, recycling facilities, and landfills.
Conserving Resources through Waste Reduction
Effective waste management reduces the need to extract raw materials. Recycling and waste-to-energy initiatives help conserve resources and minimize the environmental footprint of resource extraction.
Cost Savings from Waste Reduction
Waste management programs that emphasize waste reduction and recycling can save businesses and households money. By reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills, organizations can minimize waste disposal costs. Additionally, recycling can generate revenue through the sale of recyclable materials.
Key Takeaways:
- Sewage and waste management create jobs in waste management companies, recycling facilities, and landfills.
- Effective waste management conserves resources by reducing the need for raw material extraction.
- Waste reduction programs can save businesses and households money by minimizing waste disposal costs and generating revenue through recycling.
Source: The Economic and Environmental Benefits of Efficient Waste Management
Sustainable Sewage and Waste Management Practices: A Guide
Key Takeaways:
- Proper sustainable sewage and waste management practices protect the environment, public health, and quality of life.
- Waste reduction, reuse, and recycling should be prioritized over unsustainable practices like landfilling and incineration.
- Effective waste management systems reduce pollution, climate change, and ecological footprint.
- Investing in infrastructure, education, and innovative waste technologies is essential for sustainable waste management.
Understanding Waste Management
Waste management involves collecting, treating, and disposing of wastewater and solid waste to protect health and the environment. Proper management systems prevent contamination of water, soil, and air, reducing pollution, protecting wildlife, and improving public health.
Benefits of Sustainable Waste Management
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Waste decomposition releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Sustainable waste management techniques like anaerobic digestion and composting capture and utilize these gases for energy production.
- Improved air and water quality: Improper waste disposal pollutes waterways and releases harmful toxins into the air. Sustainable practices such as wastewater treatment and proper solid waste disposal reduce these risks.
- Conserved natural resources: Recycling and composting divert waste from landfills, conserving valuable resources like wood, paper, and metals.
Steps for Sustainable Waste Management
- Invest in infrastructure: Upgrade sewage collection and treatment facilities and expand composting and recycling programs.
- Promote waste reduction and recycling: Educate the public about the importance of reducing waste, reusing items, and recycling materials.
- Implement waste-to-energy initiatives: Convert waste into renewable energy sources like biogas and electricity through technologies like anaerobic digestion and incineration with energy recovery.
Conclusion
Sustainable sewage and waste management practices are vital for protecting the environment, safeguarding public health, and promoting a circular economy. By investing in sustainable waste management systems, we can create a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future for generations to come.
Citation:
- Environmental Sustainability Impacts of Solid Waste Management Practices:
Role of Individuals and Communities in Proper Sewage and Waste Management
Individuals and communities play significant roles in ensuring proper sewage and waste management. When individuals take responsibility for their actions and communities work together, we can create a cleaner and healthier environment for ourselves and future generations.
Key Takeaways:
- Waste management is essential for environmental sustainability and public health.
- Individuals can reduce waste by opting for reusable items, practicing the 3Rs (reduce, reuse, recycle), and responsible disposal of hazardous waste.
- Community engagement is crucial for successful waste management programs, and includes outreach, education, and feedback collection.
- Overcoming barriers to waste management, such as cost and lack of access to proper waste disposal systems, requires collaborative efforts between individuals, communities, and governments.
How Communities Can Get Involved:
- Participate in waste management programs such as garbage and recycling collection, composting, and hazardous waste disposal.
- Volunteer for community cleanups and other environmental initiatives.
- Educate others about the importance of proper waste management.
- Advocate for policies that promote waste reduction and recycling.
How Individuals Can Make a Difference:
- Reduce plastic consumption and opt for durable and reusable alternatives.
- Recycle and compost as much as possible, and learn which materials can be recycled or composted locally.
- Dispose of hazardous waste according to local regulations to avoid contamination of soil and water.
- Support sustainable businesses that prioritize waste reduction and ethical waste management practices.
Working together, individuals and communities can promote proper sewage and waste management practices, reduce environmental pollution, and improve public health. By taking responsibility for our waste and working towards a circular economy, we can create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Citation:
Sewak, A., Deshpande, S., Rundle-Thiele, S., Zhao, F., & Anibaldi, R. (2021). Community perspectives and engagement in sustainable solid waste management services: A systematic review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 291, 126046.

FAQ
Q1: What are the key benefits of proper sewage and waste management?
A1: Proper sewage and waste management offer significant economic and environmental benefits, including job creation, resource conservation, cost savings, pollution mitigation, reduced ecological footprint, and improved public health.
Q2: What are the main challenges associated with waste management?
A2: Developing effective waste management systems, educating the public about waste reduction, and funding sustainable waste management practices are the primary challenges.
Q3: How can we promote sustainable waste management practices?
A3: Implementing waste reduction and recycling programs, investing in new waste treatment technologies, and promoting waste-to-energy initiatives are effective ways to enhance sustainable waste management.
Q4: What role does community engagement play in proper waste management?
A4: Community perspectives and involvement in waste management are crucial for designing effective programs, addressing barriers, improving health outcomes, and promoting environmental sustainability.
Q5: How does improper waste management impact the environment?
A5: Improper waste management can lead to health and environmental problems, including the spread of diseases, air and water pollution, and the depletion of natural resources.